

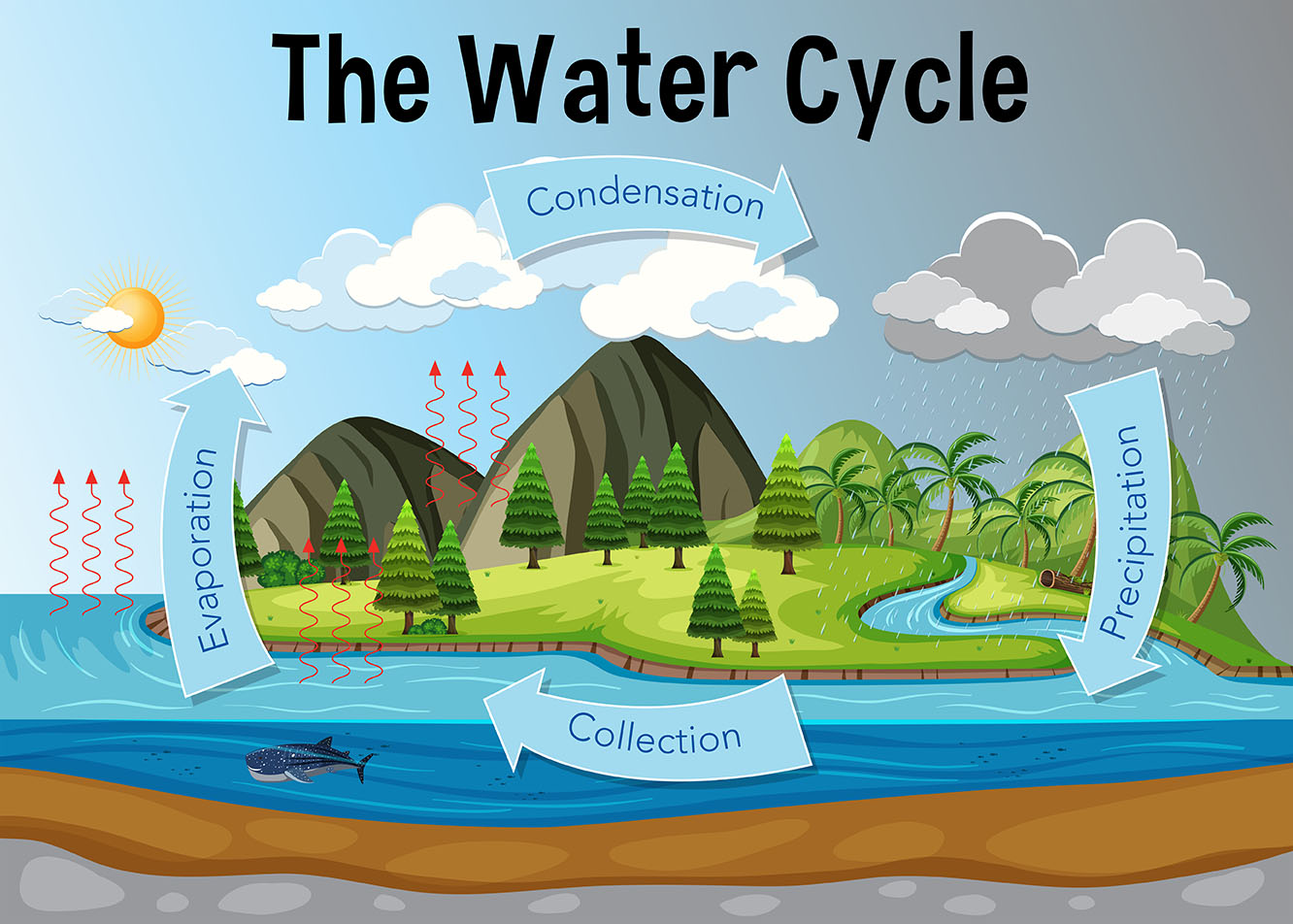
The water cycle is the continuous movement of water around the Earth. It is made up of four main steps: evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and collection.
Evaporation is when water turns into a gas. This happens when the sun heats up the water and the water molecules start to move faster. The faster the water molecules move, the easier it is for them to escape into the air.
Condensation is when water vapour turns back into a liquid. This happens when the water vapour cools down and the water molecules start to slow down. The slower the water molecules move, the more likely they are to stick together and form clouds.
Precipitation is when water falls back to Earth. This can happen in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
Collection is when the water collects on the ground or in bodies of water. This water can then be used by plants, animals, and people.
The water cycle is essential for life on Earth.
Noun: the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
Adjective: relating to the water cycle.
The word "water cycle" comes from the combination of the words "water" and "cycle".
The word "water" comes from the Old English word "wæter", which means "water".
The word "cycle" comes from the Greek word "kyklos", which means "circle".
The first recorded use of the word "water cycle" was in the 19th century.
What are the stages of the water cycle?