

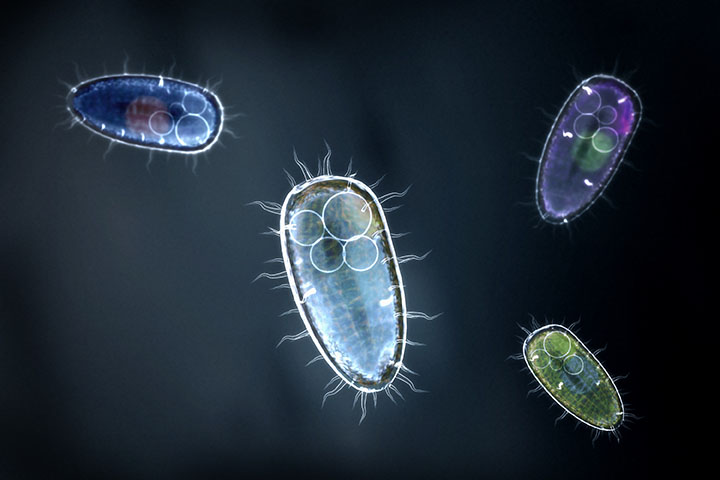
An organism that is made up of only one cell is called a unicellular organism. Unicellular organisms are the smallest and simplest organisms.
Some examples of unicellular organisms include bacteria, algae, and protozoa. Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that can be found everywhere in the environment. Algae are simple plants that can be found in water or on land. Protozoa are single-celled animals that can be found in water or soil.
Unicellular organisms are able to perform all of the basic life functions, such as eating, breathing, and reproducing, within their single cell. They do this by using specialized parts of the cell, such as the nucleus, the mitochondria, and the chloroplasts.
Bacteria are unicellular organisms.
Adjective:
Noun:
The word "unicellular" comes from the Latin words "uni" (one) and "cellularis" (of or relating to a cell). The word "unicellular" was first used in the 19th century.
What is a unicellular organism?