

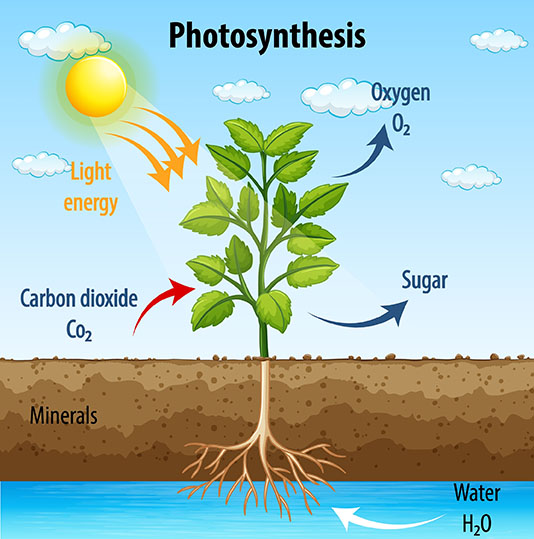
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight to make food. Plants take in carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil. They use these substances to create glucose, a type of sugar. Glucose is used by plants for energy and to build other molecules, such as proteins and starch.
Photosynthesis happens in the leaves of plants. The leaves have special cells called chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is a green pigment that absorbs sunlight. When sunlight hits chlorophyll, it causes electrons to become excited. These electrons are then used to power a series of chemical reactions that create glucose.
Photosynthesis is an important process for life on Earth. Plants are the only organisms that can produce their own food. This means that all other organisms, including humans, rely on plants for food. Photosynthesis also releases oxygen into the atmosphere, which is essential for animals and other organisms to breathe.
The process of photosynthesis is essential for life on Earth.
Noun:
Adjective:
The word "photosynthesis" comes from the Greek words "phōs" (light) and "synthesis" (putting together).
The word "photosynthesis" was first used in English in the 19th century. It was used to refer to the process by which plants use sunlight to make food.
The word "photosynthesis" is a compound word, made up of the words "photo" and "synthesis". The word "photo" comes from the Greek word "phōs", which means "light". The word "synthesis" comes from the Greek word "synthesis", which means "putting together".
So, photosynthesis literally means "putting together with light". This is a reference to the process by which plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and energy-rich carbohydrates.
What is photosynthesis?