

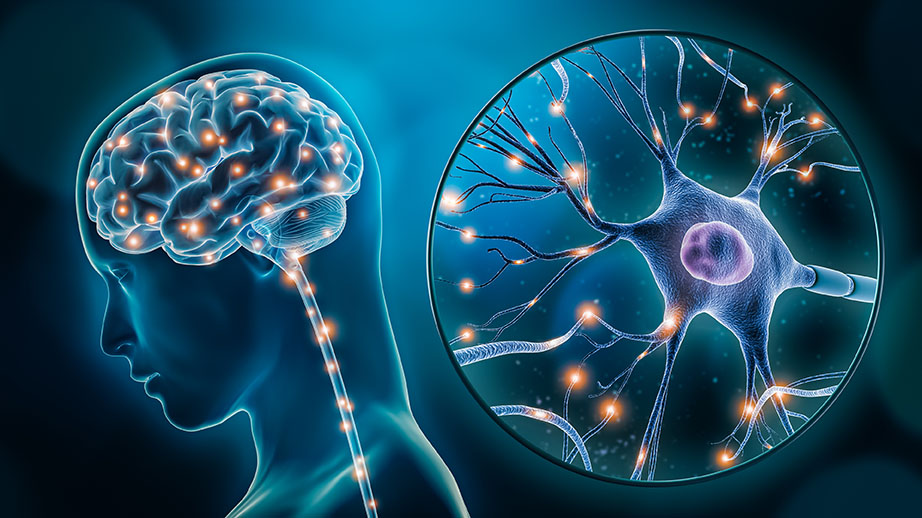
A nerve is a long, thin bundle of fibres that carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body. Nerves are made up of cells called neurons. Neurons are the body's "electrical wires". They carry messages in the form of electrical signals.
Nerves are found all over the body. They connect the brain to the skin, muscles, and organs. Nerves allow us to feel things, move our bodies, and control our organs.
There are two main types of nerves: sensory nerves and motor nerves. Sensory nerves carry messages from the body to the brain. Motor nerves carry messages from the brain to the body.
When we touch something, sensory nerves send a message to the brain. The brain interprets the message and tells us what we are touching. When we want to move our arm, motor nerves send a message from the brain to the muscles in our arm. The muscles contract and our arm moves.
Nerves are essential for our survival. They allow us to interact with our environment and control our bodies.
The word "nerve" comes from the Latin word "nervus," which means "sinew, tendon, cord, or bowstring.".
Noun: A long, slender, threadlike structure that carries impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and other parts of the body.
Adjective: Relating to nerves or the nervous system.
Derivative: Nervate, nerveless, nervous.
The word "nerve" comes from the Latin word "nervus," which means "sinew, tendon, cord, or bowstring." The Latin word "nervus" is derived from the Proto-Indo-European root *ner-," which means "to twist.".
The word "nerve" was first used in English in the 13th century. It was used to describe the sinews or tendons that connect muscles to bones.
What is a nerve?